Using product management frameworks is a way to dramatically improve product management and make your products a success. Read on to find the most powerful frameworks you can use to boost your business.
Have you ever wondered how international giants like Amazon, Apple, and Shopify can deliver a wide range of successful products that almost always do well in the marketplace? It’s because these companies rely on a well-structured product management system to ensure that each of their products meets customer needs.
Product management frameworks are an integral component of the product management process. They help managers flesh out their production process into methodologies and steps teams follow to increase the likelihood of success of each product the company creates.
If you want to master product management, you have to pick the right framework. Here are the top ten product frameworks your business can use to help increase the success rate and customer appeal of your products.
What is a Product Management Framework?
A product management framework is a guide to creating a new product or expanding an existing one. The framework consists of a series of steps that companies can follow to ensure that they build a successful product in a cost-effective, timely manner.
Product management frameworks are a tool for companies to utilize the information they gained from the past.
Frameworks also allow companies to understand the steps that were taken to build a successful product so that they can continuously improve their process. The approach is similar to using a recipe; once you have the basics down, you can make a few tweaks to improve it.
Benefits of Product Management Frameworks
- Product management frameworks improve product management by improving decision-making. You will make better decisions faster.
- Frameworks include data from previous products, such as customer feedback; this project history data enables companies to turn consumer preferences into prioritized features, improving product definition and product/market fit.
- Product management frameworks assess the market and provide companies with data regarding current trends that enable them to respond rapidly to change.
- Using product management frameworks helps companies decrease development costs and save cycle time.
What are the Different Types of Product Management Frameworks?
Below is a list of product management frameworks as used by leading companies; you will need to tailor these frameworks to your market, products, and corporate culture.
Strategic Frameworks and Product Development
Strategic frameworks focus on selecting the best product development investments among a set of proposed projects. Companies use strategic frameworks to improve product strategy, ensuring that product development projects have product/market fit, are compatible with your product portfolio, and have a clear path to profitability.
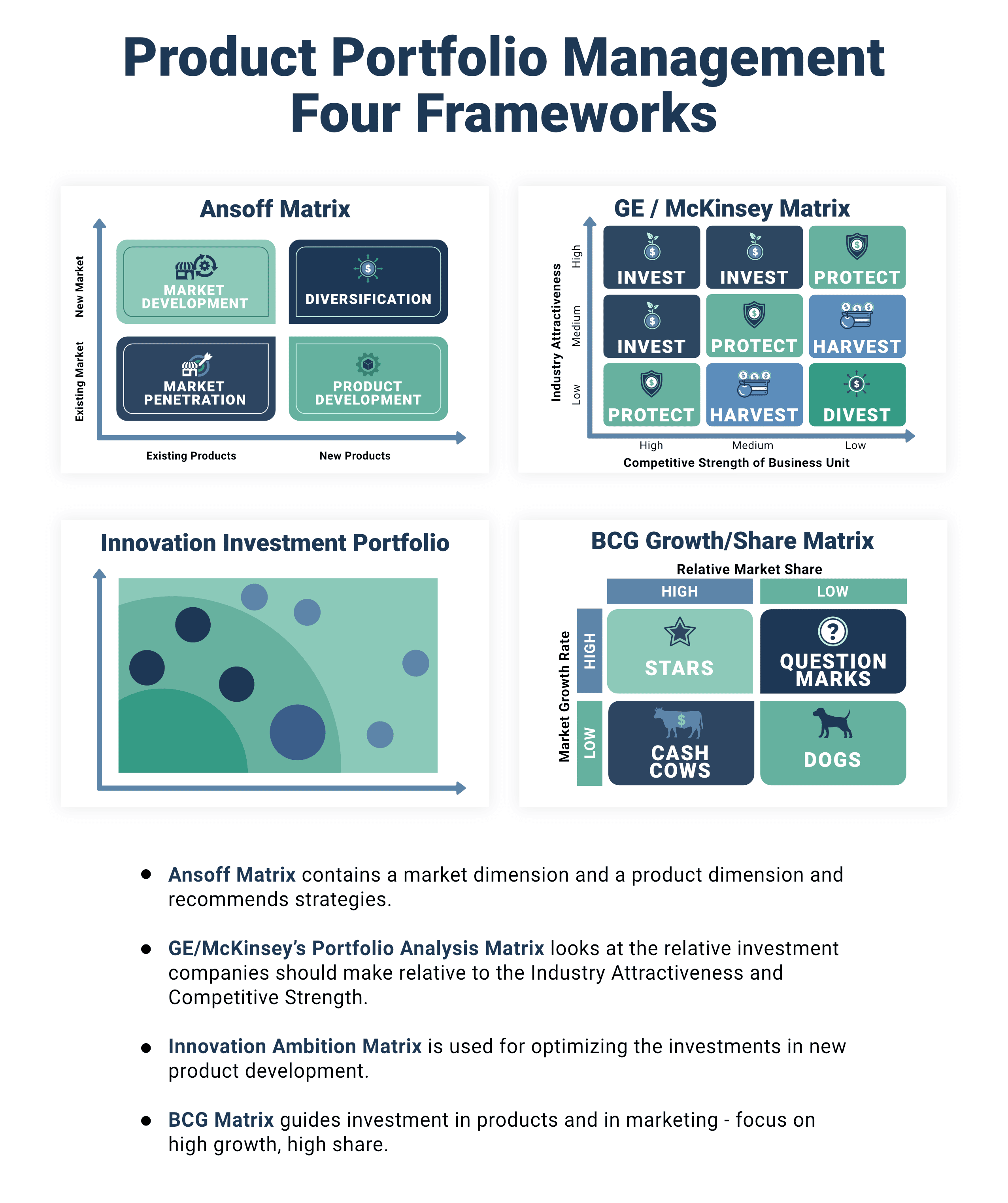
Strategic Product Management Frameworks: Examples
1. BCG Growth-Share Matrix
The BCG Growth-Share Matrix is a strategic product management framework that helps companies determine their most profitable investments among prospective projects.
The BCG Growth-Share Matrix categorizes high-growth and high-share projects as ‘Stars’ and helps companies identify these opportunities. Low-growth and low-share opportunities are termed ‘Dogs’, and company investments that can be taken off the table. Low-share and high-growth opportunities are termed ‘Question Marks,’ while low-growth and high-share opportunities are termed ‘Cows.’
The primary use of a BCG Growth-Share Matrix is to lead companies to invest in ‘Stars’ and stay away from ‘Dogs.’ The BCG framework is commonly used by companies that have multiple businesses to branch out into different markets.
2. GE/McKinsey’s Portfolio Analysis Matrix
The GE/McKinsey Portfolio Analysis Matrix is a strategic product management framework that also focuses on guiding product development investments.
The key feature of the GE/McKinsey Portfolio Analysis Matrix is its ability to factor in internal and external elements to generate a successful investment strategy. It compares potential investments to external market factors like the popularity and success of the industry and the strength of competitor products/brands.
This strategic framework generates a holistic view of the company and its market environment. It is most commonly used by larger corporations.
3. Ansoff Matrix
The Ansoff Matrix is composed of a grid that consists of a market component and a product component.
The market quadrant/component maps existing markets and new markets, while the product quadrant maps existing products and new products.
The matrix helps firms determine whether they want to invest in a conservative manner or a more diverse manner. A conservative investment would focus on investing in the growth of existing products in existing markets, while a diverse investment strategy would focus on investing in new products in new markets.
The Ansoff Matrix is a good strategic framework used by companies for shaping their general investment policy.
4. Innovation Ambition Matrix
An Innovation Ambition Matrix is a strategic product management matrix that focuses on guiding companies in investing in the creation of new products.
The framework operates on the basis of a matrix that has three components: “Core,” “Adjacent Innovations,” and “Transformational Initiatives.”
The “Core” focuses on guiding companies in investments that cater towards innovation in existing products.
The “Adjacent Innovations” focus on investments in new products that are similar to already existing products created by the company.
The “Transformational Initiatives” grid helps guide companies to invest in completely new projects. This component is great for coming up with fresh designs that cater to a new audience.
The Innovation Ambition Matrix is a type of strategic framework that is a great fit for tech companies that prioritize the development of unique new products.
5. Product Management Lifecycle Framework
The product management lifecycle framework consists of the following phases:
- Coming up with the concept/idea for a new product, which involves the creation of a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) as an initial iteration of the product
- Testing the new product idea
- Developing the product concept
- Running a market analysis on the developed product concept
- Streamlining the production process
- Testing the finished product
- Entering the product into the market and advertising it
The Product Management Lifecycle Framework essentially manages the entire production process, from the conceptualization of a product to its entry into the market, to its eventual retirement. It is a concise strategic framework that companies use to oversee a product throughout all the phases of its life. If you want to gain a more development-focused framework, product development life cycles.
6. SWOT Framework
The SWOT framework is a strategic product management framework that focuses on analyzing the ‘Strengths’, ‘Weaknesses’, “Opportunities’, and ‘Threats’ related to a company’s strategic enterprise.
The SWOT framework is used by companies to determine whether investing in a strategic enterprise would be beneficial or not. A strategic enterprise may consist of launching a new product or branching out into a new market.
This framework is based on a grid that breaks down any new strategic endeavor into its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. The company then analyzes the data generated by the framework and decides whether or not it would be favorable to pursue the initiative.
7. Business Canvas Framework/ Product Strategy Canvas Framework
The Business Canvas/Product Strategy Canvas framework is a strategic product management framework that guides design teams in coming up with an effective product development strategy.
The framework uses a canvas that consists of the following elements:
- The primary business partners of your company
- The fundamental projects that are a part of your company’s product development process
- The function of the product your company is creating
- The main target audience that your product is targeting
- The primary resources you will utilize in the production process
- How you plan to sell your product to your customers
- The total financial cost of developing and distributing your product
- The estimated revenue you expect from the sales of your product
8. AARRR Framework
The AARRR (Acquisition, Activation, Retention, Revenue, Referral) acronym is a strategic product management framework that is specifically made for startups and small-scale businesses that want to expand.
AARRR consists of the following components:
Acquisition: developing a plan to attract new customers.
Activation: working to ensure that your customers have a good first experience with you.
Retention: executing strategies that ensure that the customers who have used your product once will buy it again.
Revenue: earning money from customers.
Referral: employing strategies in product design that ensure that your customers recommend your product to others as well.
Illustrative of the diverse landscape of product management frameworks are the Moscow Method and the Circles Method, which exemplify applying analogous principles through distinct techniques. These methodologies, renowned for their efficacy, give practitioners valuable strategies for prioritization and decision-making. Notwithstanding their disparate approaches, both methods underscore the significance of systematic analysis, enabling individuals or teams to streamline processes and attain optimal outcomes. Consequently, these frameworks serve as invaluable resources for product managers seeking structured approaches to manage and deliver successful products proficiently.
Customer Discovery Frameworks
Product teams use Customer Discovery frameworks, leveraging the analysis of buyer personas, to help the company stay in tune with consumer preferences, address pain points, and fulfill market needs during the product development process.
These frameworks focus on identifying customer problems so that companies can design their products to solve these problems and satisfy customer needs.
Customer Discovery Frameworks: Examples
1. Customer Journey Map
A Customer Journey Map is a discovery framework that analyzes the customers’ experience with a product. This framework depicts the customer’s journey while using a product.
A customer journey framework maps all the stages of a customer’s experience with a product, from the initial engagement with the company to actually buying and using the product.
Because of its detailed record-keeping, a customer journey map can provide companies with valuable data regarding how their products are perceived and how easily users can buy and use them.
2. Jobs-To-Be-Done Framework
The Jobs-To-Be-Done framework is a customer discovery framework that helps companies develop products that are guaranteed to satisfy customer needs.
The framework operates based on recognizing a specific need or job that customers have and then coming up with strategies that can help complete that job through their products.
Jobs-To-Be-Done focuses on understanding the expectations customers actually have when they buy a certain product. The framework aims to prioritize the needs of the customer throughout the product development process.
Jobs-To-Be-Done is one of the most effective frameworks for enhancing a company’s understanding of the needs of its target audience and ensuring that its products align with those needs.
3. Customer Empathy Map Framework
The Customer Empathy Map Framework is a customer discovery framework that gathers information about customers to enhance a company’s understanding of its target consumer base.
The framework presents the data it has collected in the form of concise and comprehensive charts and maps so that the product development team has a good understanding of their customers before they begin the production process.
The following are the constituents of a customer empathy map framework:
- Data regarding the customers’ thoughts and feelings. This means being aware of the customers’ primary concerns and understanding what they look for in a product.
- Data regarding where the customers are getting their information from so that companies can create effective marketing and sales campaigns. For example, it is important to know whether customers are learning about products through social media, television, magazines, or online ads.
- Data regarding any factors that would dissuade the customer from buying the company’s product. The aim is to decrease any frustrations the customer might feel when using their product.
4. Design Thinking Framework
The Design Thinking framework focuses on enhancing companies’ understanding of their target customer base so that they can make innovations that satisfy customer needs.
The framework emphasizes organizing the steps involved in product designing to streamline the process and make it more efficient. Along with this, design frameworks are used to come up with unique, innovative product designs that are sure to do well on the market.
Thus, the Design Thinking process consists of the following stages:
- Empathizing
- Defining
- Ideating
- Prototyping
- Testing
- Implementing
Design/Process Frameworks
Product design teams use Design/Process frameworks or UX (user experience) product management frameworks to flesh out a suitable product design.
The framework focuses on organizing the steps involved in product designing to streamline the process and make it more efficient. Along with this, design frameworks are used to come up with unique, innovative product designs that are sure to do well on the market.
We have listed below the most popular design frameworks that are currently in use.
1. Lean Startup Framework
This framework for startups focuses on designing new products for an already established market. In an established market, a target consumer base is already there, and less money has to be spent on marketing the product because consumers are already aware of the category. This means that more resources can go toward the product development process.
The framework is perfect for startups because it favors flexibility over fixed, detailed long-term plans, and it focuses on prioritizing customer needs.
2. Agile Framework
The Agile framework offers a flexible approach to product management.
The Agile framework creates an environment where different team members from the same company, including stakeholders, can collaborate to achieve common product goals. The framework is built upon the principles of the Agile Manifesto.
The Agile framework consists of dividing projects into increments known as Sprints. After each Sprint, there is a “release” of some kind, which may consist of a drawing or a demonstration for internal or external customers. Agile has developed into a host of practices, such as daily stand-up meetings and release planning derived from the world of software development.
This framework opts for a more flexible approach as compared to traditional product planning. It enables companies to constantly work on product designs and design templates, updating them according to customer preferences.
3. Minimal Viable Process Framework
The Minimal Viable Process framework focuses on promoting efficiency throughout the product development process. It provides the least amount of process required to execute the project.
The model is highly flexible and allows for constant adjustments to be made throughout the product development process. This makes the Minimal Viable Process a great framework for enhancing creativity and innovation, which has led to the framework being popular amongst startups.
4. Waterfall Process/Milestone Process Framework
The Waterfall Process/Milestone Process framework takes a linear approach toward product management. It focuses on developing a product systematically from start to finish.
The Waterfall Process follows a successive pattern of product development, similar to the flow of a waterfall, in the sense that each step is fully completed before the next one begins.
This is a traditional design model that focuses on generating a detailed development plan before production begins.
5. Product Roadmaps
Product Roadmaps lay out the vision and objectives of your product set so that companies can align their products around clear strategic goals.
Product Roadmaps draw out a map for companies to follow during their design process and production phases. The framework helps in prioritizing features, managing resources, and maintaining a product backlog, ensuring a systematic approach to product development and continuous improvement throughout the lifecycle.
Prioritization Frameworks
Prioritization frameworks help your company to streamline your product development process after your company has decided which project it is going to execute. These frameworks are used to determine which tasks take priority.
1. RICE Scoring Framework
The RICE scoring framework assesses products based on the RICE criteria: ‘Reach’, ‘Impact’, ‘Confidence’, and ‘Effort’.
A product is evaluated and assigned a score in each of these four categories, and then an overall grade is determined based on its RICE scoring model. Products that achieve a high RICE score are deemed high priority, indicating their significance and importance in the product roadmap and prioritization process.
2. Storytelling/Story Mapping Framework
The storytelling/story mapping framework is one of the primary prioritization product management frameworks. It focuses on relaying each customer’s experience with the product in the form of a ‘story’.
Product managers integrate these individual stories to paint an image of the customers’ general experience with the product. Not only does this framework help companies understand their customer base as a whole, but it also depicts how each customer’s ‘story’ contributes to the combined consumer response to the product.
The storytelling framework builds upon a customer’s experience with a product in the way a story would progress. The first step is to determine the main character of the story, that is, identifying your customer. The next step focuses on the conflict in the story, which means identifying the product’s purpose and any problems associated with it. This phase also includes finding solutions to these problems and putting them into practice. The last part of the story, its ‘end’, focuses on the results you achieve from your implemented solutions.
When the entire storyboard is complete, companies can gain insight into which stories offer successful solutions, which is an easy way for them to figure out which stories to prioritize.
3. KANO Framework
The KANO framework is a prioritization product management framework named after Japanese professor and quality management consultant Noriaki Kano.
The framework is useful in helping companies determine and prioritize the features of their products that bring customers the most satisfaction.
The KANO graph displays four grids that help companies determine which features of an effective product will boost customer satisfaction and which features will boost customer delight. This graphical representation provides an easy way for developers to identify and prioritize features that will increase their product’s popularity in the market. Utilizing the KANO model aids in making informed decisions about feature development and allocation of resources.
4. Quantitative Market Research Framework
The Quantitative Market Research framework involves generating questions that help companies collect quantitative data relevant to their target customer base.
The framework uses techniques like surveys, polls, and questionnaires to gather data that can provide insight into customer needs. This information is used to prioritize consumer preferences throughout the product development process to ensure the popularity of the end product.
What Product Management Frameworks Do Successful Companies Use?
Here’s how large, innovative companies use product management frameworks to develop a stream of successful new products.
1. Spotify’s Experimentation Framework
Spotify is one of the leading music streaming platforms in the world, amassing a total of 406 million active users worldwide in 2021.
Spotify relies on an experimentation framework to ensure the success of its products. Its framework consists of six groups, called ‘squads’, that have around twelve members each. Each squad works on a project in an area of their specialty.
Although Spotify’s squads give its workers more room for independence and experimentation, they are highly collaborative. Each squad knows what the other teams are working on so that there are no replications during product designs.
All of the squads follow a framework that revolves around these steps:
Think it – This is the brainstorming phase for each squad. They come up with product design concepts and track customers’ potential reactions to those products.
Build it – The squads start working on a model for their product.
Ship it – Spotify tests its product on a small audience to see how they respond to it.
Tweak out – This is the most time-consuming phase in Spotify’s framework. During this phase, teams constantly readjust product design, run market analysis, estimate customer response to their product, and work on reducing production costs as well as any risks of failure.
2. Amazon’s ‘Working Backwards’ Approach
According to Ian McAllister, who used to work as a GM at Amazon, Amazon begins its product creation by describing what reaction they want the product to elicit from customers.
When they’ve come up with an idea for a product with a specific purpose, Amazon’s product managers hold press conferences to project ideas regarding the product’s design and features. The goal is to come up with features that they feel would help get the desired response from the customer. This approach allows them to gather feedback or user stories and generate buzz around the upcoming product. By sharing their vision through press releases, Amazon aims to refine and shape the features of the product based on the desired customer response.
For product managers at Amazon, this phase is crucial and often the most time-consuming. Andy Jassy, the head of Amazon’s Web Services, reported to the Financial Times that he went through as many as 31 drafts for press conferences that discussed product features.
Once they’ve discovered a successful idea, Amazon teams work backward, starting from the product vision and mapping out the process required to bring it to life. By employing this approach, Amazon ensures that the entire product development process revolves around the desired customer response. This method allows them to build a product that is purposefully designed to elicit specific reactions and meet customer expectations.
3. Shopify’s Product Growth Framework
Shopify uses multiple product management frameworks, but the most popular one is the ‘Product Growth Framework’, which was built by its general manager, Sylvia Ng.
The framework consists of the following eight steps,
1. Understanding the level at which your company and product exist
Focus on understanding the level at which your company is operating and how you want your product to fit into that. This phase is important in ensuring that your product is compatible with your company.
2. Figuring out your objectives
This stage involves determining the main objectives you want your product to achieve before you start working on it. This is to ensure that you can build a product with features that help bring you to your objectives.
3. Modeling your product
This phase deals with the customer response to your product. You will determine how customers will use your product, why it would be desirable to them, and how it could satisfy customers.
4. Establishing your primary metric
Establish the main metric you will be using to measure your product’s success. The metric you choose depends on whatever goal is the most important to you.
5. Formulating a prioritization system
This phase involves brainstorming to come up with a grid of prioritized features and tasks.
6. Deriving goals
This stage involves coming up with tangible goals you want your product to achieve. These could include earning a set amount of profit, growing your business by a particular percentage, or increasing your customer popularity.
7. Working on product creation
This phase is at the beginning of product creation, and it involves setting up the equipment and system you need to work on your product.
8. Gathering a development team
The last stage involves picking out a team that covers all your bases, from product development to marketing, to computer engineering. Your team needs to be well-equipped to deal with the product creation process from beginning to end.
Conclusion
Whatever type of products your company specializes in creating, it is imperative for you to have a product management framework to optimize workflows, effectively communicate the value proposition, and ensure the success of your product.
The type of product management framework you choose to use depends on your company, the product you want to create, and the goals you want it to achieve.
What is important to realize is that using a framework is essential in aiding product management and increasing the chances of your product being a success. You can even use multiple frameworks if you think that would work best for you. Consider discussing this with a product development consultant.
Frameworks provide a map that allows you to:
- Invest in the right products
- Design around customer needs and,
- Develop a complete portfolio that is consistent with your markets and your appetite for risk.

